By Tijani Musa.
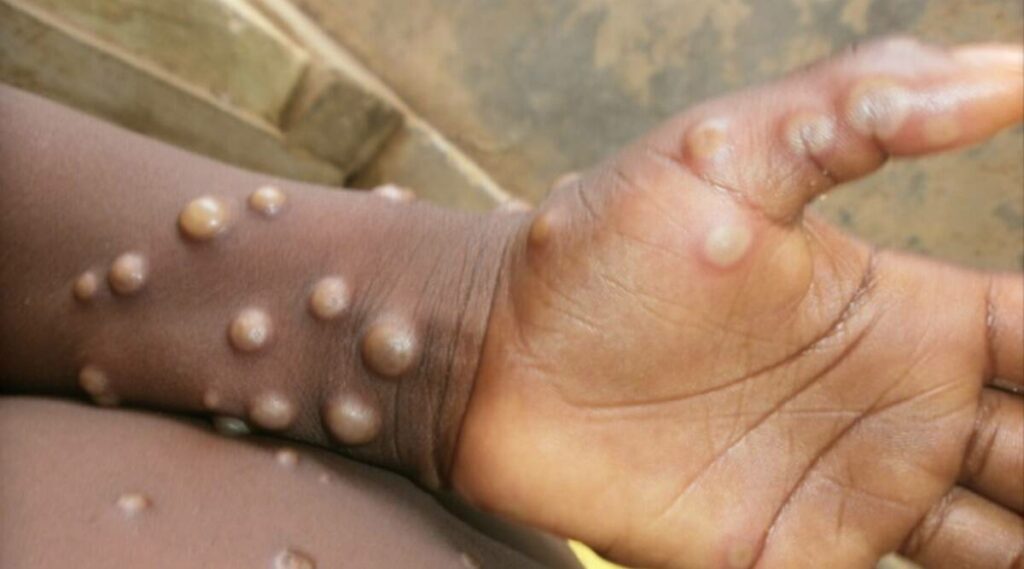
Monkeypox is a viral zoonosis (a virus transmitted from animals to humans). According to the WHO, the symptoms of monkeypox are similar to those seen in the past in smallpox patients, although the monkeypox symptoms are clinically less severe. Another significant differentiation is that smallpox was known to have been eradicated in the 1980s. Due to the subsequent cessation of the smallpox vaccination following the eradication, monkeypox is making an entrance and attracting the attention of public health practitioners, everywhere. Historically, the environmental conditions in which cases of monkeypox are detected are near tropical rainforests. These environmental conditions are mainly in central and west Africa. Nonetheless, if Covid-19 pandemic has taught humanity any lessons, it would be that we live in a connected world and humans are interdependent on each other. Subsequently, a disease in the tropical rainforests of west Africa could easily travel on the next flight to infect the next person anywhere in the world. Hence, to minimize the potential spread of monkeypox is to understand the people, place, or things susceptible to carrying and spreading the virus.
Typical host of monkeypox virus
Various animal species are susceptible to the monkeypox virus. The WHO included rope squirrels, tree squirrels, Gambian pouched rats, dormice, non-human primates, and other species as likely hosts of monkeypox. There is still mystery lingering on the history of the monkeypox virus, and further studies are being conducted to learn more about its exact reservoir (s) and its circulation.
How does it spread
Monkeypox spreads in many different ways starting from person to person through:
- Direct contact with the infectious rash, scabs, or body fluids
- Respiratory secretions during prolonged, face-to-face contact, or intimate physical contacts, such as kissing, cuddling, or sex
- Touching items (such as clothing or linens) that previously touched the infectious rash or body fluids
- Pregnant people can spread the virus to their fetus through the placenta
- At this time, it is not known if monkeypox can spread through semen or vagina fluids
According to the CDC, it is possible for people to get monkeypox from infected animals, either by being scratched or bitten by the animal or by preparing or eating meat, or by using products from an infected animal. Monkeypox can spread from the time symptoms start until the rash has fully healed and a fresh layer of skin has formed. The window of illness typically lasts from 2-4 weeks. In the United States, the CDC latest data shows at least 2,108 probable or confirmed cases as of July 19, 2022. The U.S is working diligently to get in front of this virus as it has tripled its monkeypox vaccine doses since last week. More work is needed to increase the supply of vaccines.
Dr. Anthony Fauci warns that “this is something we definitely need to take seriously. We don’t know the scope and the potential of it yet, but we have to act like it will have the capability of spreading much more widely than it’s spreading right now.”